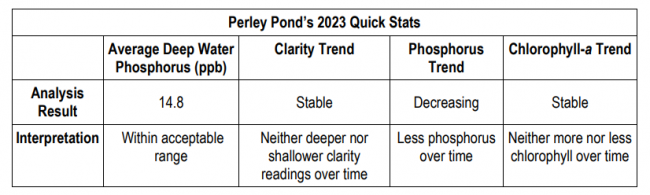
Perley Pond is sampled by LEA once per year in August. The long-term average reflects data from 1996 to 2023. The Secchi disk reading for 2023 was 4.5 meters, which falls into the moderate clarity range. The total phosphorus reading of 7.7 ppb falls into the moderate range. The average deep water phosphorus value was less than 10 ppb above average surface water phosphorus values, which suggests phosphorus recycling is not problematic. The chlorophyll-a reading of 8.4 ppb falls into the high range. Long-term trend analysis indicates chlorophyll-a concentrations are stable, total phosphorus concentrations are decreasing, and clarity readings are stable. Gloeotrichia echenulata colonies were not observed in Perley Pond in 2023.
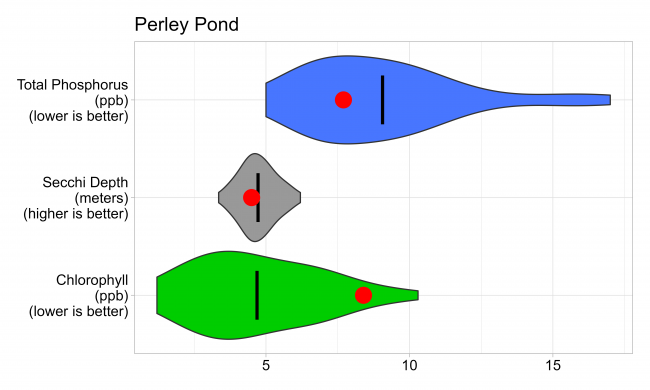
Perley Pond’s surface water chlorophyll (ppb), phosphorus (ppb), and Secchi depth (meters) data comparison. Colored areas represent the long-term range of values, from minimum to maximum. Area thickness indicates frequency of measurements at that value. Area thickness increases as more measurements are reported at that value. The vertical black line represents the long-term average value. The large red dot represents 2023’s average value.
Gloeotrichia echinulata (a type of cyanobacteria (blue-green algae) commonly found in low-nutrient waters) can be seen with the naked eye. Gloeo density is reported as a value ranging from 0 – 6, based on the number of Gloeo colonies seen through a Secchi scope. Higher values indicate more Gloeo colonies. Gloeotrichia echenulata colonies were not observed in Perley Pond in 2023.